ΑΡΘΡΟ ΤΟΥ ΚΑΘΗΓΗΤΗ ΜΑΣ ΔΡ. Μ. ΕΥΡΥΠΙΩΤΗ ΣΤΟ
LEADERSHIP & ORGANIZATIONAL MANAGEMENT JOURNAL
TECHNOLOGY INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION PRACTICES IN INTRA-ORGANIZATION TRAINING: PROPOSALS FOR FULL SCALE USE OF COMPUTER-BASED LEARNING AND BUSINESS DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEMS
(21-22 Σεπτεμβρίου 2007)
John Mylonakis
10 Nikiforou str., Glyfada
166 75, Athens, Greece
Michalis Evripiotis
Senior Manager, OTE
4 Aghisilaou str., 166 75, Glyfada
Athens, Greece
Apostolos G. Christopoulos
University of Athens
Department of Economics
5 Stadiou str., 10562, Athens, Greece
ABSTRACT
The incorporation of Information and Communication Technologies in enterprise training procedures improves the quality of training and reduces time. The traditional model of creating and offering a training program through the Internet is not enough to describe today's situation and its future perspective. The systems and tools for the support of inter-company learning are relatively new in the field of Information Technology and provide researchers with a new way to incorporate innovative ideas and technologies of the business world. Intranets are the fastest growing section of the Internet market, as more and more enterprises understand the importance of the use of technology, in order to carry out internal communications. The management of relational databases containing plenty of information has become a useful factor for achieving enterprise objectives, as well as, inter-company training. Neural nets and decision trees are some of the most used tools and techniques in data mining.
Keywords: Information and Communication Technologies, Inter-Company Training, Knowledge Management, E-learning, Hypertext Technologies, Data Mining-Technologies, Neural Networks
1. Introduction
The generalized use of New Technologies and particularly computers in daily and personal practices has greatly affected the training procedure within enterprises. The role of the trainer has been significantly diversified, as training should include all those elements required, so that people have the ability to participate, act and perform tasks within modern enterprises.
The incorporation of Information and Communication Technologies in enterprise training procedures improves the quality of training and reduces time. Information is transmitted in a more direct manner, the trainer avoids time-consuming procedures, such as repetitions or correcting tests, while distance learning becomes possible. Thus, new technologies help trainers and complete their educational work (Kyriazis & Bakogiannis, 2003).
The cope of this paper is to present several technological means, with the right scheduling, can be used successfully not only by smaller companies but also by large organizations, in order to facilitate internal learning.
2. Reasons that make inter-company training necessary
The reasons that make staff training indispensable relate to changes or prevailing situations in the external or internal environment of a company. Indicatively, some of these changes are:
- Technological progress: requires new specialties and knowledge, the application of new methods and procedures for the completion of projects.
- Consumer demands and needs: requires job positions with new or different characteristics (quality, variety, easiness, speed, personal service, new products or services).
- Mergers and acquisitions: require new organizational cultures, new job positions, different content of projects.
- Re-structuring of operations and organizational changes: require new responsibilities, extended tasks, diversified content of projects.
- Performance gap and ineffective use of production resources, due to staff inadequacy or their differences in terms of value systems and their attitude towards work (Prior J., 2000).
3. Computer-based training
Computer Based Training (CBT) constitutes an effective and flexible learning method which may be used at all staff levels (Vrettaros, 2004).
CBT Advantages
- Employees can process the training material at their own pace.
- It is directly available at many different areas of an enterprise and may be adjusted depending on work commitments.
- It might become a cost-effective means to meet their training needs.
- Allows for new teaching methods.
- It encourages the effective use of time and resources.
- Gives trainees the opportunity to know their progress.
- Usually, the training takes place in a personal mode; however, employees with similar training needs can work together. The exchange of ideas, notions and questions improves learning.
- Cohesion in training is diffused across the company.
e-Learning
The expansion in the use of Internet and the dynamics of the World Wide Web is currently a social phenomenon. The traditional model of creating and offering a training program through the Internet is not enough to describe today's situation and its future perspective. The dynamics of training activities that are developing based on the World Wide Web lead to a new approach in this field.
E-Learning (electronic learning or web learning) is defined as the use of new technologies, multimedia and the Internet, with the aim to improve the quality of learning through accessing methods and learning services, such as distance communication, exchange and cooperation (European Commission, e-Learning Glossary, http://www.elearningeuropa.info).
The Advantages of e-Learning
- Possibility to have distant access to the training material.
- Allows learning access just in time (exactly when it is needed).
- Offers the trainer alternative access options.
- Possibility of managing and maintaining the systems centrally (more flexible management).
- Possibility of cooperation between trainers and trainees.
- Less transportation costs (in Bibliography it is mentioned that over 40% of training costs involve transportation).
- Less facilities and equipment costs (equipment, furniture, etc.).
- On-time delivery of learning services to all participants (with the same quality).
The advantages of computer-based learning are the same also in this case, with the exception that in e-Learning all courses are provided distantly.
In order to name an organization as "learning organization", it should be well-trained in the creation, acquisition and dissemination of knowledge, as well as in adjusting its behavior, in such a way as to absorb and diffuse knowledge, issues, thoughts and experiments. The requirements for all the above is to plan and establish an effective learning process. Knowledge Management technologies can contribute to this, as they are considered as means of support for learning processes and mechanisms. Therefore, before a Knowledge Management platform is implemented, an analysis must have taken place for all processes that support learning in the organization.
A Knowledge Management tool must entail multiple parameters and take into account elements (Wang, Wang & Shee, 2005), such as the following:
- Network development
- Information system design
- Changes in business culture
- Creation of work groups
4. Technological platforms that support learning processes
The systems and tools for the support of inter-company learning are relatively new in the field of Information Technology and provide researchers with a new way to incorporate innovative ideas and technologies of the business world. Several existing and established enterprise technologies that have been used until today to perform many procedures can also act as tools for the support of inter-company learning processes (following the appropriate approach, analysis and parameterization).
Some of these technologies are:
- Communication and collaborative systems
- Document Management Systems
- Intranets
- Data warehouses
- Data mining – On Line Analytical process tools
- Workflow systems
- Searching and indexing tools
- Expert systems and Decision Support Systems
- Enterprise Resource Planning systems
The technologies described have not been designed specifically for the purpose of supporting learning processes within enterprises. This is due to the fact that there are no tools that have been designed and implemented for this purpose, as the interest of enterprises in tools and technologies that support learning processes is fairly recent. Analyses show that the market in this sector is still unsettled and lots of things have to be done in order for these technologies to mature. However, the technologies and systems described, after the proper processing, can create an effective technological platform for supporting inter-company training at all levels: person, group, company (Alessi & Trollip, 2005).
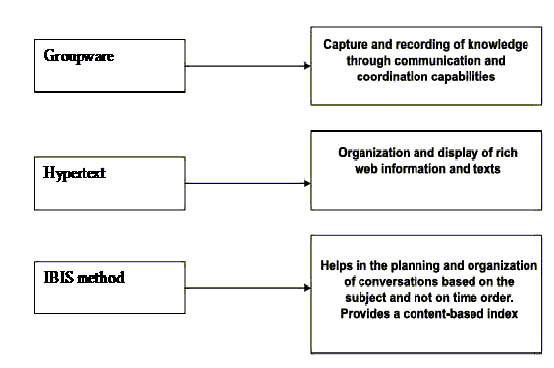
Groupware technologies
Groupware technologies have been designed to facilitate group work. These technologies are used in communication, cooperation, coordination, competition and the resolving of problems. They are divided in “real time” or “synchronous” groupware (users work together at the same time) and “asynchronous” groupware (users work at different times).
The most popular applications for “real time” or “synchronous” groupware are:
- Shared whiteboards
- Video communications
- Decision Support Systems
- Chat systems
Asynchronous groupware:
The most popular application for asynchronous groupware is definitely email. Apart from that, other applications that distinguish are:
- Newsgroups and mailing lists
- Workflow systems
- Hypertext
- Group calendars and collaborative writing systems
Another difference relates to whether users work together at the same place or in different locations. The sector engaged in design and groupware system applications is called Computer Supported Cooperative Work (CSCW). The designing of groupware technologies has considered the dynamics of groups and the way with which people behave within a group. It is necessary for the system to be adopted by all group members or by most of them, in order to bring out the advantages of this method. Furthermore, employees should participate actively and exchange opinions.
Groupware systems can constitute a means for dialogues among enterprise members and facilitate the recording of semi-structured information. By using these systems, participants will be able to exchange ideas, share experiences and take common decisions. Semi-structured information can undergo further processing and be distributed across the enterprise and can also supply the mechanisms of organizational learning.
Hypertext technologies
Hypertext technologies comply also with the non-linear nature of modern enterprises, converting texts with interconnected “hyper documents”, thus enabling the discovery of more information and knowledge. Their use is appropriate for the interconnection of ideas without the need for an explicit expression of their meaning, their relationship, etc.
Issue Based Information Systems (IBIS)
In IBIS conversations are categorized as follows:
- Issues that are reported as questions
- Positions that can offer solutions on the corresponding issues
- Arguments that support the corresponding positions
This model provides the requirements for the structuring and recording of conversations not in time order (like emails or bulletin board-type systems), but based on the issue discussed in each case, focusing on content.
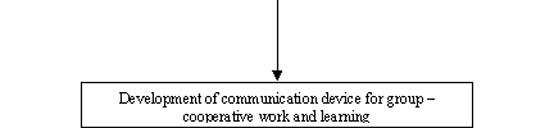
The above three technologies can be combined in such a way as to form a communication device for groups and group work within the context of enterprises. Such communication devices can record and interconnect unstructured, informal or/and formal discussions and present them in a visualized mode. This way, they enable the classification and strengthening of the rather unclear process of group work within the context of enterprises.
Intranet technology
Intranets are the fastest growing section of the Internet market, as more and more enterprises understand the importance of the use of technology, in order to carry out internal communications. This is a technology which, using a cost-effective way, diffuses information and knowledge within an enterprise, thus significantly improving communication capabilities. Before each attempt to implement related technologies, it is necessary to achieve good planning and detailed recording and understanding of internal communication needs within the company, followed by familiarization with the appropriate tools.
A properly planned internal communications mechanism is considered as a prerequisite for the support of enterprise learning. The main installation system consists of a server platform and World Wide Web server software. On the clients’ side, it is necessary to have the proper browser software. The TCP/IP communication protocol is used, thus also offering the advantages of the Internet. This type of interconnection protocol is not intended to replace the possibly installed LAN or WAN, but to cooperate smoothly with it, thus completing its communication capabilities. Some of the advantages of its use are the following:
- A World Wide Web server platform can support both internal applications (dissemination of knowledge within a company) and external (Internet marketing, communications).
- Through the use of World Wide Web open and flexible technology, enterprises disseminate information and knowledge in effective ways and costs.
- Authorized users can have access to the World Wide Web server and to receive knowledge managed in distance, eliminating any geographical restrictions.
- The use of client browsers (with a standard windows interface) provides the possibility to easily complete other applications, such as e-mail, fax, calendars, videoconferencing, etc.
- World Wide Web technology used in Intranets can be easily completed by multimedia applications, a fact that is deeply desired in relation to learning processes.
5. Data Mining Technologies and On Line Analytical Processing (OLAP)
OLAP Technologies
The management of relational databases containing plenty of information (both routine and important) has become a useful factor for achieving enterprise objectives, as well as, inter-company training. They are mostly used in fields such as the management and testing focusing on OLTP transaction processing. Relational database systems are used as tools for the development of data warehouses. One system stores regular information by various resources, answering the questions "who" and "what" regarding past events (http://www.astd.org/astd,
http://hbswk.hbs.edu/archive/3483.html, http://www.swan.ac.uk/cds/rd/ccdb.htm,
http://www.co-i-l.com/coil/knowledge-garden/cop/olearning.shtml)
Distinction between Data warehouses and OLAP
Data warehouse systems are usually based on relational technology, while OLAP systems use a multidimensional view of collective data, in order to provide fast access to information of strategic importance that can undergo further processing and analysis. OLAP systems convert "raw" data in such a way as to reflect the real multidimensional view of the company as perceived by each user individually. Their main strength lies in their ability to answer "what if" and "why" questions, distinguishing them from data warehouses. OLAP systems, therefore, allow for the analysis of both past and future scenarios.
Characteristics of OLAP systems that can support learning processes
- Speed and performance
The answer to the questions submitted by users in an OLAP system must be direct, however complex.
- Multidimensional data/ consolidation paths
Consolidation is the process of composing information bits in simple knowledge groups, a fact that is of interest to learners as they attempt to compose and interpret information and convert it to knowledge. The highest level in a consolidation path is a data dimension. The possibility to have more than one hierarchies without creating data inconsistencies is critical in OLAP systems.
- Dynamic analysis of data
From the moment the data have been loaded in the OLAP system their analysis may begin. Dynamic analysis can help understand the changes in a company and to detect possible solutions to emerging issues.
- Ability to retrieve data from various sources
OLAP systems should provide the possibility to retrieve information from different sources (relational databases, legacy systems, flat files, etc.). This way, users can rightly and fast search for information and acquire knowledge.
- Visualization of results/ business data
A system must provide all necessary tools for the visual presentation of the results of the analysis and business data, thus forming an attractive tool for trainees.
- User transparency
OLAP system users do not need to have specialized knowledge to perform the desired analysis, a fact that has a positive impact in their willingness to use the system (http://www.astd.org/astd, http://hbswk.hbs.edu/archive/3483.html,
http://www.co-i-l.com/coil/knowledge-garden/cop/olearning.shtml,
http://www.swan.ac.uk/cds/rd/ccdb.htm)
Data Mining Technologies
Data Mining or Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD) is the retrieval of internal, previously unknown, useful information from data. This includes several technical activities (clustering, data summarization, learning classification rules, etc.). Its greatest achievement is its ability to detect certain more generalized patterns and relations among data, with the use of special techniques and the construction of abstractive reality representation models. With regards to inter-company training, the contribution of data mining methods is of great importance, especially in data interpretation processes.
They are characterized by stages that describe how "raw" data are converted to knowledge. The stages of knowledge discovery are:
- - Selection
- - Preprocessing
- - Transformation
- - Data Mining
- - Interpretation Evaluation
- - Knowledge
Data Mining is the stage during which certain modeling techniques and advanced statistical analyses are applied in data, in order to deduct useful templates and relations. On the other hand, the knowledge discovery method as a whole is indispensable because it describes all the necessary steps in order to secure semantically useful results (http://www.elearningeuropa.info, http://www.nbg.gr,
http://www.geniki.gr, http://www.atebank.gr,
http://egnatiasite.egnatiabank.gr,
http://www.emporiki.gr,
http://www.bankofcyprous.gr,
http://www.pireausbank.gr).
Neural Networks
Neural nets and decision trees are some of the most used tools and techniques in data mining. Using certain advanced learning algorithms they become an important factor that enables learning processes within a learning environment. Neural nets use parameters to structure various models, in order to estimate and combine prices and to predict definite or continuing prices. They consist of three levels: input, hidden, output.
The architecture of a neural network is characterized by the selection of input and output variables, the number of nodes, hidden levels and their connection. The user is expected to select the number of nodes, the number of hidden levels, the activation function and weight limits. This particular type of systems cannot undergo processing by a broad variety of users within a company; it is mostly addressed to specialized users. However, it is a technology that is considered as a primary tool for many different kinds of applications and may constitute a main technological component in a completed inter-company learning network. Neural nets entail a different philosophy than that of many statistical methods, as they usually have more parameters compared with a standard statistical model. An important advantage of neural networks is that they can easily applied to parallel computers, every node carrying out calculations at the same time.
Decision trees
Decision trees represent a series of rules that lead to a specific price or decision. They have become particularly popular due to their precision and easiness to understand, in contrast with neural networks. Decision trees used to predict categorical variables are called classification trees, while those that predict continuous variables are called regression trees. A decision tree has the ability to explain its predictions, as every path is directly visible and comprehensible. Yet, as they grow in size, their explanations and interpretations become more and more complex. Many groupware and collaboration software use decision trees and their techniques for representing concept maps, knowledge models, etc.
Learning with the use of multimedia
In the last years and within the field of Instructional software tools, people refer to the advanced use and application of multimedia applications, as well as, the combination and incorporation of traditional methods to Computer Based Multimedia Applications. The term "multimedia" has been used to describe a computer system that combines text, graphics, images, sound, motion, video, etc. Of major importance is the feature of user interactivity with the learning system (Alessi & Trollip, 2005).
The main multimedia components are the following:
- Text
It constitutes the most frequently used means because it is easily produced easy-to-use, flexible, it has less requirements in terms of resources (e.g. storage) and bandwidth (as in the case of broadcasting via networks). On the other hand and based on the principles of human-machine interaction, extended use should be avoided, as combined with the static nature of this means, it can discourage and strain the user. Yet, most people receive information and knowledge by reading text. Thus, it is implied that by using such means, the ability of learners can be strengthened, namely their information gathering and structuring skills.
- Image
This is a very important and effective means, which serves two main objectives: in terms of aesthetics, learning becomes more attractive, a fact that is thought to motivate users/ learners. In terms of strengthening cognitive abilities, the system presents the examined subject to the user/ learner in a more eloquent and effective way. Using an image can provide a more realistic impression of the examined situation and its parameters, thus allowing for an improved interpretation of available information.
- Animation
Animation is a tool that cannot be used in a paper-based case study. Typical uses of this powerful means include the demonstration of the sequence of procedures within an organization, future business processes and changes, information flow in organizations, as well as the flow of physical or digital products, etc. Through graphic techniques, it is considered to strengthen the procedures of knowledge acquisition and information interpretation.
- Diagrams, tables, forms
Diagrams, tables and forms are used as a supplement to text, simplifying and enhancing it. More specifically, such means may illustrate in a more effective way than text the following:
- - Relations among objects
- - Demonstration of operational procedures
- - Demonstration of a company’s hierarchy and processes.
Diagrams above all are thought to be very effective in explaining theories and complex data – information, contributing to the improvement of the information interpretation process.
- Video
This is a very powerful and technologically advanced resource, as in reality it constitutes a combination of text, sound, graphics and motion. It is extremely effective when inducing the learner to watch it and understand the various facts, concepts, etc. However, it is very demanding in resources, while particular attention should be paid in excessive loading of information contained. It affects the process of acquiring knowledge, while it may facilitate the information interpretation process.
6. Technologies and Internet Standards that can strengthen the inter-company video-learning process
The most important technological standards on the main multimedia features are described below:
Audio
The primary technological standard audio used are:
-WAVΕ (.wav): It is the main standard used in windows environments and other platforms.
-MPEG 3 (mp3): This is the most popular audio data compression technology
-ΑU, AIFF: It is an audio format used on the Internet (less frequent than the former).
Video
The main standards are:
-Audio/Visual Interleaved Data (.avi): It is a standard for windows environments.
-QuickTime Movie (.mov): It is a video format used in Apple systems, as well as other platforms in the form of plug-in.
-Motion Picture Experts Group (.mpeg): Emerging standard that is continuously growing and is run through specialized software or decoding device.
Graphics
The main graphics standards are:
-Joint Photographic Experts Group (.jpeg): This is a very good graphics standard and produces effective compression.
-Graphics Interchange Format (.gif)
-Animated Gif (.gif): It constitutes a series of separate gif files that are combined (visualization through browsers).
Active Server Pages (ASP)
Active Server Pages (ASPs) are a technology used in Microsoft web servers. This technology offers the opportunity of dynamic extension and page changes by using Visual Basic scripts, which are easier to program by Java.
HTML/DHTML
Dynamic HTML (DHTML) technology is a new proposal by Internet Society who has acknowledged that the constantly growing number of web pages and their inter-operability requires more than simple HTML. DHTML offers an improved way to present web pages. The use of DHTML does not lead to big differences regarding browsers (Internet Explorer, Netscape Navigator) and allows for easier modifications.
Streaming Video
The Streaming Video technology (streams of video information) constitutes a reliable solution to the problem of transmitting extremely large video files, as it provides high data compression, as well as fast and precise transmission of video. Well-known examples of this technology are Microsoft Netshow and Real Networks Realplayer. A disadvantage of this technology (based on current conditions) is the fact that the quality of transmission is satisfactory only for the audio part of the files. The presenting of streaming video on the Internet is still in a preliminary phase. This is not also the case with CD-ROMs and intranets.
Further technological features
For designing interactive tools, the following are used:
The traditional Internet standard protocols (TCP / IP, FΤP, ΗΤΤΡ).
- A necessary technological component is web browsers and various plug-ins, which are autonomous programs that strengthen browser functionality and increase the interaction level that they can offer. Usually, popular Java Applets are used, which are designed in C, C ++-type languages.
- Miscellaneous: It involves the designing and use of various types of extensions operable within Web environments. Well-known are also Virtual 3D environments (e.g. VRML).
Video-learning pilot application
Initiating the development of a video-learning application, we must never forget that the point of focus is learning. Learning and didactic methods are the main issue and are applied through the support of new technologies. The main aspect that learning material creators have to deal with is how and which procedure should be used to convert the learning material into video-learning material. The instructor’s work and pedagogic methods acquire a new dimension. The instructor’s work remains the most important; however the instructor himself is transferred behind the line. The physical absence of the instructor is replaced by a series of communication practices with the use of multimedia and computers.
Process of Video-learning pilot application
The process of applying video-learning programs tales place in two phases:
1. First Phase: During the first phase, the learning package is created and the video-learning environment is designed.
2. Second Phase: During the second phase, a pilot application of learning tools is carried out.
6. Conclusions
Rapid technological developments have formed a new climate, which has increased the responsibilities of company/organization managers for additional training of staff. Public education refers to the preparation of an individual as a citizen, rather than as an employee. The viability of an organization depends on its capability to learn faster from its competitors. This can be achieved with systematic and long-term effort, in order for employees to become adequately trained and to be able to meet the company’s objectives in the best possible way. The largest part of human resources that enter the labor market every year requires training for the completion of any project.
All employees ought to continuously extend their knowledge, in order to be able to meet the requirements of the market and the society. Many projects are cancelled due to the fact that the staff is incapable of meeting its requirements. Many changes that are necessary for the re-organization of a company are suspended due to the fact that the staff cannot accept them. Such problems can be resolved by continuously training, informing and updating staff knowledge. This responsibility on the part of enterprises for providing staff with constant knowledge and skills is more and more acknowledged as an investment in human resources.
Yet, despite the general recognition and acceptance of the value of training and developing human resources, only a few companies in Greece are seriously engaged in this issue. While people invest millions in real estate, facilities, machinery, offices, material and computer software, they neglect to invest in people, i.e. the most important factor that forms, uses and produces added value to all physical production materials.
REFERENCES
Alessi S. & Trollip S. (2005), “Multimedia and training. Methods and Development”,
M. Giourdas Publications, Athens
Kyriazis A. & Bakogiannis S. (2003), “The use of new technologies in training.
Coexistence of didactic activities and technology”, Athens
Prior J. (2000), “Training & Development”, ELLIN Publications, Athens
Vrettaros G. (2004), “Learning through computer networks and the cyberspace”,
Kleidarithmos Publications, Athens
Wang Y. & Wang H. & Shee D. (2005): «Measuring e-learning systems success in an organizational context: Scale development and validation», Computers in Human Behavior, Volume 23, Issue 4, pp. 1792-1808
http://www.elearningeuropa.info
http://www.nbg.gr
http://www.geniki.gr
http://www.atebank.gr
http://egnatiasite.egnatiabank.gr
http://www.emporiki.gr
http://www.bankofcyprous.gr
http://www.pireausbank.gr
http://hbswk.hbs.edu/archive/3483.html
http://www.co-i-l.com/coil/knowledge-garden/cop/olearning.shtml
http://www.swan.ac.uk/cds/rd/ccdb.htm
http://www.astd.org/astd
επιστροφή
|